How to Cite | Publication History | PlumX Article Matrix
R Malekpoorafshar1, M Karvar2, M Mohammadi3, M M Hayran3, R mirzaee4
1Pathologist, assistant professor, kerman university of medical science, kerman, iran. 2urologist,assistant professor, jiroft university of medical science, jiroft, iran. 3specialist in emergency medicicne,kerman university of medical science, kerman, iran. 4phD, lecturer, jiroft university of medical science, jiroft, iran.
ABSTRACT: Organophosphate compounds have been used as Pesticides in agriculture from a long time ago. The most common cause of death by these compounds is the related pulmonary complications. Since there have seen no study about the effects of dexamethasone on the reduction of mortality caused by Organophosphate poisoning and its pathologic effects on lungs, we decided to study this matter. this research was done on rats.40 rats were randomly divided into two groups of control and treatment. Both groups were injected 25 mg/kg of Dichlorvos poison subcutaneously. The control group was injected 0.5 ml of physiological Saline and the treatment group was injected 100 mg/kg dexamethasone intraperitoneally. Then the rats of each group were analyzed separately for the rate of mortality and apnea. The lungs of the sample rats were sent to pathologic unit for further analyzing. The information was analyzed using spss 17 and chi square statistic test. Significant level was considered 0.05.in treatment group 10 rats (50%)survived while in control group all the rats were died which shows that the mortality was significantly higher in control group (p Value = 0.033(. the average time period to mortality was also significantly higher in control group. The results had a significant difference in first class vascularcongestion(p Value = 0.007( and second class hemorrhage (p value = 0.046) between the two sample groups. As a general conclusion it seems that dexamethasone can somehow reduce the destructive effects of Organophosphate poisons in alveoli and reduce the mortality significantly.
KEYWORDS: dexamethasone; Organophosphate poisons; rats; death rate; pathologic effects
Download this article as:Introduction
Organophosphatecompounds have been used as pesticides in agriculture and also in chemical weapons. The most common cause of hospitalization due to pesticide poisoning is for being in contact with Organophosphate poisons (above 80% of the cases). 3 million individuals are being poisoned with these poisons annually and 250 thousand of them die (1).The death because of Organophosphate poisons is multifactorial but the main reason is pulmonary complications. Organophosphate compounds inhibit the Cholinesterase enzyme and result in aggregation of Acetylcholine on the surface of neural-muscular receptors, so their effects are appeared(2). The most common manifestations of Organophosphate poisoning are: hyper-salivation, increase of pulmonary mucus, running nose, diarrhea, in continence of urine, bronchial spasm,vomiting andmyosis. Extra-aggregation of mucus in airways and in pulmonary alveoli is one of the main reasons of mortality in these patients(3). Despite the enormous progresses made in medical science,treatment o fOrganophosphate poisoning haven’t changed in the last 50 years and it mainly includes Atropine,Oximes, Benzodiazepines and respiratory support(4). The latest studies have revealed other mechanisms rather than Acetylcholinesteraseinhibition like acute inflammation in Organophosphate poisoning syndromes emergence(5). The relationship between being in contact with Organophosphate poisons and emergence of asthma symptomsand the increasing of airways stimulation have been revealed in new epidemiologic and clinical studies(6).Since there have seen no studies about the effects of dexamethasone on the reduction of mortality caused by Organophosphate poisoning and its pathologic effects on lungs, we decided to study this matter.
Methods
this is an experimental study and it has been done on rats. 40 adult male rats with the approximate weight of 200-250 grams were divided into two groups of 20. The rats of each group were in the same state of living circumstances,temperature, water, consumed food and lightening and darkness cycles. Both groups were injected 25 mg/kg of diluted Dichlorvos poison in 0.09% saline subcutaneously. The cause of using this amount of the poison was for making sure of the death of all the rats of control group. In the same researches, using this dose caused death in 100% of control group in 12 minutes. Rats of control group received 0.5 ml of normal saline Intraperitonealy one minute after being injected with the poison. Rats of treatment group received 100 mg/kg dexamethasone Intraperitonealy one minute after receiving poison. Then both groups were analyzed for mortality and the time period of apnea. If a rat stayed alive for 120 minutes it was considered as a survived one. Their lungs were sent to pathology unit for further investigation. The sent samples were kept in 10% formalin for 24 hours. After preparing a block and a 5 micron slice of the samples, they were colored using H&E method. The pathologist reported at least 10 fields regarding the severity of inflammation and existence of parameters like Tissue necrosis.
Results
10 rats of the treatment group survived (50%), while all the control group rats died, which shows a significant difference between the two groups (p value=0.033).The average time of motality in treatment group was 20/20±1/48 and in control group was 15/00±2/74, which is less than treatment group(p value = 0.002)(table 1).
Table 1: the average time of mortality In pathologic samples of dead rats these matters were observed
| Group | Number | Average | Standard deviation | P Value |
| Treatment | 10 | 20.2000 | 1.48324 | 0.002 |
| Control | 20 | 15.0000 | 2.74874 |
The results showed that perivascularinflammation (p value=0.164),inflammation of the peribronchi (p value=0.500),neutrophilicexudation (p value=0.400), and alveolar wall thickening (p value=0.087) and hemosiderin existence (p value-0.806) don’t indicate a significant difference between the two groups.But first degree vascularcongestion was significantly more in control group (p value=0.007)(table 2 and Diagram 1)
Table 2: Frequency of first degree perivascular congestion in the analyzed samples
| group | P Value | |||
| treatment | control | |||
| First degree Vascular congestion | Slight | 5.0% | .0% | 0.007 |
| mediocre | 35.0% | 5.0% | ||
| Severe | 10.0% | 45.0 | ||
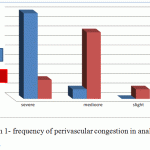 |
Figure 1: frequency of perivascular congestion in analyzed samples |
Second degree hemorrhagewas also significantly higherin control group (p value=0.046)(table 3)
Table 3: frequency of second degree hemorrhage in analyzed samples
| Group | P Value | |||
| Case | control | |||
| Second degree hemorrhage | none | 15.0% | 5.0% | 0.046 |
| slight | 30.0% | 20.0% | ||
| mediocre | 5.0% | 15.0% | ||
| severe | .0% | 10.0% | ||
Discussion
in this experimental study there were 20 rats in each group. Rats of control group were injected with normal saline in addition to poison and rats of treatment group were injected with dexamethasone besides poison.
Dexamethasone is a strong Anti-inflammatory drug which prevents thehyper-excitability of airways in case of being in contact with Stimulatingantigens. Prescribing dexamethasone can prevent the dysfunction of m2 muscarinic receptors (which is one of the mechanisms of allergic reaction increase in airways)(7).
In a study done by DU et al, it was revealed that prescribing sodium aescinate (which has anti-inflammatory and Anti-oxidative effects) can prevent the pulmonary damages of organophosphate poisoning (8). In another study done by Proskocilet al, it was revealed that organophosphate poisoning can result in the Release of TNF-α from Pulmonarymacrophages, the increase of allergic reactions in airways and the dysfunction of m2 muscarinic which can be prevented by prescribing Etanercept(a TNF-αInhibitor)(9).
This study revealed that the death rate is significantly less in control group and the time period to mortality is significantly more in treatment group.The pathologic results also revealed that perivascularinflammation, Inflammation of the peribronchi, Neutrophilin filtration, Alveolar wall thickening and Hemosiderin existence don’t have a significant difference between tow groups, but first degree perivascularcongestion and second degree hemorrhage was significantly more in control group.in a study done for this matter it was revealed that prescribing dexamethasone before being in contact with Parathion, which is an organophosphate poison, can increase Hepatic clearance from this poison by Induction of CytochromeP3A23 enzyme (10).
Dinis-Oliveira et al revealed in a related study that prescribing a high dose of dexamethasone for the rats that were in contact with paraquat poison (which cause death byRespiratory failure) can reduce the mortalty and improve the pathologic effects in treated rats (11). So it’s consistent with our study.
Conclusion
as a general matter it seems that dexamethasone can somehow reduce the destructive effects of organophosphate poisons in alveoli and also reduce the mortality significantly. Because of the limitation of the number of the samples, more studies are needed to approve the results of this study.
References
- Kumar SV, Fareedullah Md., Sudhakar Y., Venkateswarlu B., Kumar AE..Current review on organophosphorus poisoning.Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2010, 2 (4): 199-215.
- Gaspari RJ, Paydarfar D. Pathophysiology of respiratory failure following acute dichlorvos poisoning in a rodent model. Neurotoxicology. 2007 ; 28(3): 664–671.
- Eddleston M, Buckley NA, Eyer P, Dawson AH. Management of acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning.Lancet. 2008; 371(9612): 5. 607-697.
- Zhang ZQ, Liang R, Huang T, Yang HX, Peng W, Li F,et al. Dynamic change of vascular active materials and inflammatory mediums after acute organophosphate poisoning and its clinical significance. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2003; 15: 7. 762-763.
- Qu AJ, Wu TJ, Tian H, Zou XL, and Zhang BJ. Dynamic change of serum TNF-alpha in patient with severe acute organic phosphorus poisoning complicated by respiratory failure. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2005; 23: 153-154.
- Ouyang YH, Li SL, Song W, Zhao N, and Ma ZF.Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on tumor necrosis factor-alpha in liver and spleen in mice with acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2010; 22: 238-239.
- Evans CM, Jacoby DB, Fryer AD. Effects of dexamethasone on antigen-induced airway eosinophilia and M(2) receptor dysfunction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001 May;163(6):1484-1492.
- Du Y, Wang T, Jiang N, Ren RT, Zhao DL, Li C, Fu FH. Protective effect of sodium aescinate on lung injury induced by methyl parathion. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2011 Oct;30(10):1584-1591.
- Proskocil BJ, Bruun DA, Jacoby DB, van Rooijen N, Lein PJ, Fryer AD. Macrophage TNF-α mediates parathion-induced airway hyperreactivity in guinea pigs. Am JPhysiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 Apr 15;304(8):L519-529.
- Hurh E, Lee E, Lee A, Kim Y, Kim S, Kim S, Lee M. Effects of enzyme inducers or inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous parathion in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2000 Jul;21(5):193-204.
- Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Duarte JA, Remião F, Sánchez-Navarro A, Bastos ML, Carvalho F. Single high dose dexamethasone treatment decreases the pathological score and increases the survival rate of paraquat-intoxicated rats. Toxicology. 2006 Oct 3;227(1-2) :73-85.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





