How to Cite | Publication History | PlumX Article Matrix
Human Resources Management models for recruitment of faculty members: A critical review
Soleiman Ahmady1, Farin Tatari2*, ShahramYazdani3 and Seyed Ali Hosseini4
1Department of Medical Education, School of Medical Education. Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 2Department of Occupational Therapy, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran Corresponding Author's Email: farintatari@yahoo.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bbra/2049
ABSTRACT: Nowadays, the growth and development of organizations depend on real utilization of human resources, human resources is considered the organization's most important asset and their effective management is the key to the success of the organization. In higher educational system, faculty members are one of the main assets and the success of organizations is due to the desired efficiency of them. Effective search, and recruitment of faculty members are a critical matter for the university and should be managed in such a way that the right people are tenured as faculty members. In this study a critical review is used as an effective methodology for conceptual originality. Related words were selected and extensive and structured search of texts has been done. 250 articles and text were retrieved. Then purposive sampling was conducted in order to screen the texts and articles follow by three phases: (A) the preliminary phase or title screening base on that the title of texts should be related to the faculty members’recruit management. (B) The secondary phase was performed according to a summary and introduction of text study. (C) and in the tertiary screening phase: articles and texts were studied briefly and related articles were prioritized based on conceptual and textual richness,according to the research subject, and irrelevant articles were excluded from the study. Full and in-depth study of the most richness papers was begun. 50 articles were analyzed and synthesized and finally the study product was presented in the form of a model. The research findings showed that by using a13-step systematic process of selection and recruitment, having a proactive, capable and versatile recruitment committee, setting a description of the position based on merit and competency, using new and diverse applicant tracking methods, advertising based on competency , evaluating applicants with new Competency-based and value-based interviews methods and adopting competency-based recruitment model, can make the achievement and recruit of worthy and capable forces in the university possible.
KEYWORDS: Human Resource Management (HRM) , faculty member, recruitment, search,critical review
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Ahmady S, Tatari F, Yazdani S, Hosseini S. A. Human Resources Management models for recruitment of faculty members: A critical review. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 2016;13(1) |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Ahmady S, Tatari F, Yazdani S, Hosseini S. A. Human Resources Management models for recruitment of faculty members: A critical review. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 2016;13(1). Available from: https://www.biotech-asia.org/?p=7787 |
Introduction
Human Resource Management means strategic and sustainable management and administrate with the most valuable asset of an organization which means its employees who have been working on it and helping the organization to achieve its goals (1). The general purpose of human resource management is to ensure that the organization will able to be successful in helping its employees. Human Resources Management is responsible for several tasks, including selection, recruitment, development and retention (2) and the selection in the most important process that is done by the Human Resource Management (3). Search, recruitment, and selection of employees with high potential will be started with finding the right people and choosing the right employees and contributes to the success of an organization. Personnel recruitmentis a process of selecting those that have the best compatibility with the required determined qualifications to perform a specified role and task. This process determines the quality of the input staff and plays a key role in human resources management (4). Reviewing the evolution of human resources management theories suggest that theories have been maturing during a hundred years and have been finding a scientific status (5).
The resource-based theory that today in strategic human resource management literature has a great importance is based on the principle that the competitive advantage in an organization will achieve on the basis of the valuable resources,set of the organization and the employees are the main source to improve the quality and Productivity (6). According to this theory, Nowadays, the growth and development of organizations depend on correct application of human resources and human resources is considered the most important asset of the organization and their effective management is the key to the success of an organization (7). In higher education system, the faculty members are one of the main assets that are responsible for specialized human resource training and providing scientific and research services. Thus, the development and growth of higher education institutions is due to the favorable performance of faculty members and poor performance will lead to a crisis in the evolution and development of institutions and ultimately their removing from the academic competition, which this process leads to the lack of development. An appropriate and effective human resources management system can increase the efficiency and organizational performance through an effective management of faculty members. Search, selection and recruitment of faculty members are vital and strategic issues for universities and must be managed in such a way that merit and efficient people will be placed in faculty member position and have been able to play a decisive role in achieving the goals of higher education (8).
In medical sciences universities that are somehow responsible for the health of society, faculty member management, especially their recruitment method is important, because the effectiveness of teachers may lead to provide graduates, according to professional specific standards that enter the health care system and through the Health, promotion and hygiene would provide further development. Reviewing the current system of recruitment of faculty members in Iran is the explainer of challenges such as lack of proper guidelines and techniques to attract and employ qualified and efficient forces, the inability of a core recruitment to correct identification and evaluating the capabilities of the applicants, lack of using new evaluation methods and diminished the role of stakeholders in the recruitment process (9). Given the importance of attracting and recruitment, we decided to carry out a critical review on how to recruit and select faculty members and which available models are effectives.
Materials and Methods
A preliminary review was carried out, that showed the number of articles and documents are non-research and commonly for non- research documents, review methods will be used. The review has the variety and since the goal was to achieve a degree of conceptual innovation and synthesis, a critical review methodology was used. In a critical review, at first texts were widely and extensively searched and then their quality will be evaluated critically. Articles of evaluation has been identified beyond the texts’ mere description and has been involved a degree of analysis and conceptual innovation. Articles after a brief survey and study will be ranked based on the conceptual and textual richness on the subject of the research and a deep study and survey will begin from the most richness articles. Analysis and synthesis of the articles were performed and the study product will be offered in a basic model. This model may have been a synthesis of existing models or a completely new interpretation of the available data (10).
According to the study topic, related vocabulary was selected and extensive and structured research of texts was conducted. 250 texts and articles were obtained at this stage. Then, according to purposive sampling, texts and articles screening was conducted in three stages: (A) initial or title screen, on the basis that the title of texts will be relevant to the management of faculty members’ recruitment. (B) Secondary screening, which was performed according to the study of summary and the introduction of texts. (C) Tertiary screening: At first, the articles were briefly studied and related articles were prioritized based on the conceptual and textual richness on the subject of research, and irrelevant articles were excluded from the study. Then a full and deep study was begun from the richest articles. 50 articles were analyzed. Analysis and synthesis of the articles were performed and the study product was presented in a basic model.
Ethical Considerations
The current study was approved by the ethics and research committee of Shahid Beheshti University Medical of Sciences.
Results
The research results show that universities use processes that have different stages to recruit and their faculty members’ recruitment. For example, the process of recruitment of several universities in the world is as follows:
UCLA Berkeley: 1. Forming a variety-searching committees 2. Determining the description and specification of the position 3. Post Ads 4. Determine the recruitment criteria 5. Review past searches 6.Reviews applicants source in terms of diversity (race, ethnicity and gender) 7. Review the applicants’ file 8. Prepare the initial list of applicants 9. Evaluation of the initial list applicants 10. Finalize the short list 11.Interviews (11).
Karolinska Institute at Sweden: 1.Needs Assessment 2. The appointment of search and recruitment committee 3. Create a timetable 4. Ads and media recruitment 5.Conduct the first interview and set a shortlist 6. Conduct the second interview 7. Check the references 8. Decision (12)
University of Western Australia: 1. The appointment of recruitment committee 2. Definition of the position 3. The position ads 4. Reviewsapplicants’ source in terms of diversity 5. Consensus on the Selection techniques, weight of scales, the interview questions 6. Check the resumes 7. Conduct the interviews and seminars (13).
Washington University 1. The formation of an investigative committee 2. Review the needs of the educational group 3. Job description 4. Marketing 5. Evaluate the applicants’ source 6. Determine the short list 7. Telephone interviews 8. Interview at the University 9. Check the references (14).
The results show that the search committee is one of the crucial elements in effective search of the faculty members’applicants.
In contrast to a traditional search committee, the proactive Committee model is recommended (15). In proactive search committee the composition, diversity and preparation are important. In order the committee operates effectively, a group of 5 to 9 individuals is recommended in most universities (16). The diversity in committee should be increased through considering the students, educational groups staff and faculty members outside these groups. In the composition of the committee, women and minority members must also be present (17). Preparation of the Committee is very important for effective searching. All members of the Committee should be participated in educational workshops on the search process and fair search ways (11).
Regarding the decision-making method in the search process is emphasized in most universities with the consensus method (16). The research results show the codification of specifications and description of the position is a basic step in the process that is often ignored by the search committee. The emphasis at this stage is that the committee should discuss about the issues of diversity and excellence at first and achieve a consensus. In order to reach a consensus on the purpose, responsibilities and requirements of the position and about what roles, features and merits the applicants must have, it may need several meetings. In considering the responsibilities and needs, consultation with key stakeholders, such as students is very important (16). At the stage by describing the position, using the charm makes the advertising diversity and increases the applicants’ source. We must answer these questions: 1. What should we offer so that to attract excellent and capable applicants? 2. What salary packages can attract the best applicants? 3. What are the important points of the position, institution or our society? Collecting the answers to these questions will determine the list of factors that can be used.
Position ad content is important. For example, in the University of Utah, the advertising included the following matters: the intended rank or title of the position, the intended field or expertise, special education requirements, experience or any knowledge, skills and required ability, individual tasks, the length of appointments, employment path, the deadline for receiving the application and addresses. The university statement will be attached to all advertising (18).
The research results show the wording and writing ads to recruitment diverse applicants is important. Institutions that have succeeded in recruiting diverse applicants have shown flexibility in their positions’ ads. For example, the University of Maryland used the flexible wording method as follows: Applicants must have an advanced degree in counseling or a related field (rather than consultation degree is required).
Emphasizing on the affirmative action (e.g. emphasis on women and minorities) is a form of flexibility in wording the position ads. For example, the ads’ wording in University of Michigan is as follows: the University is responsive to the needs of couples who are both employed.
Many universities such as Nottingham and Johns Hopkins use ads based on capability in order to recall. The ad includes the skills, capabilities and experiences in relation to jobs (19).
Our research results show that universities have used a variety of methods to find applicants. At the University of Florida the following actions are performed: 1. Ad in professional publications 2. Sending notices to other universities 3. personal contact to encourage people to apply 4. The employment activities at professional meetings and conferences 5. Professional consultant with top talent bank 6. Ad in the newspaper 7. Advertising in the organizations, publications and web sites focused on women and minorities 8. Online advertising on the sites (17).
The Committee should determine the recruitment criteria. In the opinion of Middlewood and colleagues, the faculty members’ recruitment criteria may include the following items: biographical data such as qualifications and experiences, technical and management skills, base knowledge, attitudes and values such as honesty, loyalty and others, such as interest.
Examples of recruitment criteria at UCLA Berkeley are 1. Field of research (relevance to the needs of faculty or group) 2. The usefulness of the research 3. Applicant’s research perspective on 5 years of the future 4. Presentations at conferences 5. Interest and ability in order to develop new research areas 6.Demonstrating the ability to teach specific content 7. Demonstrating the knowledge about effective teaching (Pedagogy) 8. Ability to develop new courses 9. Work experience with diverse students 10. Evidence indicates an interest to graduate and undergraduate education 11.Communication Skills 12.Demonstrating the ability as a responsible member of society 13. Research Grant receives 14. awards 15. Letters of recommendation (11).
The results show that the most common method to evaluate the faculty members’ applicants is the interview that is done in a structured way. Interviews are in two ways of the preliminary screening interview and interviews at the university. Preliminary screening interview is usually done by phone or in a business meeting and it determines who should attend on-campus interview (20). Two styles of interviews have been raised as Competency- based (20) and value-based interview for faculty members. University of Nottingham, Michigan and Western Australia use Competency-based interview, and the University of Utah use value-based interview.
Our research results show that universities use methods such as knowledge test, seminars or research presentation, conducting an experimental teaching and interviews to assess the applicants. For example, the University of Western Australia uses from interviews and presenting seminars or research to assess applicants, or Karolinska Institute carries out the assessment through written knowledge tests, interview and lectures in the classroom (12).
Research from referrals at the University of Washington and the Karolinska is common. Also at the University of Southern California (21) and Johns Hopkins, the legal Profile of an individual will be thoroughly reviewed. For example, at the University of California, items such as driving and dangerous driving offenses as well as having two wives can be adequate for unemploying in the university and the lack of candidate’s qualification (21). It is recommended to evaluate referrals for final applicants (16). Referral list must include at least one person who has been the applicant’s director;a person whom the applicant has worked closely with him and a person whom the applicant has reported. The general rule is that the applicant should at least note three representatives that have been in contact with him in the past 5 to 7 years. Questions from referrals are also in the style of competency-based (16).
At the stage of discussion and proposal, a negotiation must be happened between Heads of the educational department and faculty members about salary, finance and other issues that can affect an individual’s decision to accept the position.
At the stage of welcoming, the committee members introduce the applicant to other colleagues and they control his transforming to new job and society (17). The basic activities of this part in university are named as induction (22), which includes 1. Preliminary visit of the University 2. To obtain information about universities and faculty 3. Identify the individual’s needs in order to plan and investigate 4. Provide guidance and support beyond personal issues 5. Assign a mentor to support the person 6. Programs outside of work to meet staff (23).
Now that the systematic recruitments of faculty members were introduced, in the following, we discuss about different models to choose a faculty member that has been obtained at universities and texts review.
Johns Hopkins University that is the top university in the world, use talent management model for all its faculty members and staff and emphasize on competencies, set the position description based on the competencies and use the competency-based interviews to select. This university has defined 5 following main competencies: 1. Equity, Civility, Respect 2. Change management 3. Creativity and problem-solving 4. Excellence in mission and Service 5. Communications and Teamwork (23).
University of Nottingham emphasized in the recruitment of the faculty members on knowledge, skills and abilities, set the position description based on competencies and capabilities and use competency- based interviewe for recruitment of faculty members. This university considers core competencies (communication, collaboration, analysis and decision-making, planning, initiative, flexibility), core values (commitment, diversity, integrity, accountability) and management competency (leadership, strategic thinking, performance management) for the faculty members (19).
University of Manchester is as one of the leading universities in the field of new university management. This university has attempted to identify top people in terms of competency. These competencies include knowledge and services, interpersonal skills, ethical issues, management skills (24).
Nelson 4 rings model: This model consists of four circles. Inner Circle is personality traits that include empathy, honesty, motivation, commitment, impartiality and beliefs. The second circle is knowledge and basic skills, including content knowledge, problem solving, skills (physical, communicational, cognitional, interpersonal) and ethical behavior. The third circle is competencies that include teaching, discovery, integration and application. The last circle is the roles of faculty members include information manager, Curriculum developer, and leadership in the field, lecturer, consultant and researcher (25).
Badger model: Badger introduces another four rings model for faculty members’ recruitment. 1. The innermost ring consists of core values (role model, excellence-oriented, humility, self-discipline, the dream of building a higher education) 2. The second ring interpersonal skills, including the group making, leadership skill and management skill 3.The third ring non-objective factors, including Age, health, reputation, ability to be a role model. 4. The fourth ring qualifications and credentials, including educational background, work experience, articles and publications, awards and references. Badger believes that the core values are the most important circle in the evaluation of applicants and must be checked first (26).
Johnson’s model: Johnson provides a triangular model of teacher competence structure that consists of three main aspects: 1. Virtue 2. Ability 3.Competencies. In this model, the dimension of virtues is the base dimension. The Virtue dimension includes three components of honesty, care, support and plan. The ability dimension includes three components: cognitional, emotional and relational abilities. Competencies dimension (knowledge and skills) includes student’s development, communication, structure of the relationship, the mentor duties, inter sexes and inter race skills, respect for independence and self-awareness. Johnson considers the use of the model for the recruitment, training and evaluation at the university necessary (27).
Discussion and Conclusion
According to the study of universities recruitment processes, it seems that some steps such as a search committee formation, position ad and interview are common in all universities, but some basic steps such as needs assessment, check the past searches, or welcome the newly hired person are neglected in most universities. We believe that the following 13-steps model can be an appropriate and complete model for recruitment of faculty members:
- The appointment of recruitment committees
- Needs Assessment of educational departments
- Review the past searches
- Determinating the description and features of the position
- The applicant navigation
- Reviewing the Documents
- The initial screening interview
- Holding Exams
- Preparation and interview
- Research from other sources
- Final applicants’ assessment
- Negotiate and offering
- Welcoming the new hired person
We believe that the search committee is one of the important elements in the effective search of faculty members’ applicants and the process should begin with the appointment of the search committee. The composition, diversity and preparing of the search committee is important. In our opinion in order, the Committee act effectively and there will be a diversity of opinions, the committee should be large enough, but not to the extent that members do not feel part of the group being so, in our opinion a 5 to 9 people in a group can have an effective performance in most universities. We believe that the committee members should be diverse. Considering the students on the committee has potential benefits because students, particularly graduate students aware of research new areas and can see through the customer’s perspective to the issue. Inclusion of invited people will also allow entering different views to the recruitment process that is valuable. We believe that a diverse search committee would be more likely to identify strong applicants. About the training of committee members, in our view, in addition to the search process and practices, training on dealing with recruitment bias, is also important because many studies show that even people with good will and disinterested are biased in evaluation and many defaults that are due to the history and cultural history of the individual, will affect their judgment (11). In Search Committee, the consensus method of decision-making is emphasized on the faculty members. Of course, there are other methods about group’s decision-making, including decisions of the leader, the majority vote and to compromise. Each method has advantages and disadvantages. For example, voting is faster, but a majority does not always lead to the effective implementation or consent of the decisions. To gain consensus is long and difficult, but it can lead to more support and more satisfaction of decisions (17). We also believe that in the search process, consensus is the most favorable decision-making method, because all members agree with the decision and will support it.
We believe that the planning and needs assessment stages are the important steps in the selection and recruitment of faculty members that in most universities was not mentioned to them. University schedule is the basis of the search process. In our opinion, as Hall suggests, it should be a strategic approach to selection and recruitment. In planning, the number and type of required people, the activities of the faculty members group, the faculty members’ relation to target students, the labor market, the situation of competing organizations, demographic of faculty members and applicants and the budget situation should be noted. We believe that the review of the department to hire new faculty members is important and administrators and educational groups should use the vision and mission of the University, the 5-year plan of the University, and strategic plan of faculty and Statistics of Faculty members. In our view, values, culture and specially the university mission in the selection and recruitment of faculty members is important and should be considered at all stages of the selection and recruitment of faculty members (13 steps) and even beyond that, in all human resources activities (selection and recruitment, employment, retention, evaluation, compensation and services empowerment) should be reflected. The meaning of ouruniversity mission is the faculty mission and the mission of the education department that the applicant will be recruited and selected for it. Therefore, we believe that the selection and recruitment of faculty members should be based on the mission.
In the search process,the stage of previous searches, which in most universities did not pay attention to it, is important in the sense that we can get success factors and the failure factors of previous searches and used them in the current search.
In the codification stage,the specification of position and the need to discuss issues of diversity and excellence by the search committee, as well as Vicker, we believe that diversity and excellence, are important and related topics. The element diversity is an axial to excellence. The diversity of the faculty members and university staff will affect on the strengths and intellectual of them. Diversity in experience, age, religion, race and gender will enrich the environment for teaching and research. We believe that creating a more diverse applicant sources ensures that the best applicant is in the source.
In our opinion, determining the characterize of the position will answer the question that what knowledge, attitudes, experience, personal qualities, competencies and capabilities are necessary for success in this position and should be considered them? Search committee must first predict the considering position tasks. It should consider the roles of a successful new hired person and remember that this person may not have the exact tasks of the same previous faculty members (19). We believe that, anything about the position should be included in the description of the position carefully. In addition to the items that the University of Utah mentioned, the following issues should be noted in the description of the position: the institution and place title, a statement of the position goal, the roles and responsibilities and detailed description of the basic tasks, conditions, qualifications and core competencies, the process of application, the review process and the salary and wage range.
We believe, in determining the characterization of position and recruitment of faculty members, considering abilities and competencies, according to the role that is expected of faculty members, is important. Three elements of independence, academic freedom and the use of competence and talents are needs of the university and faculty members as the most important members of this system, have a crucial role in its success or failure. Therefore, skills, abilities, knowledge, attitude and, in a word, their competence to the success of the university is essential.Factors such as the different functions of the university, supply exceeds demand and the emergence of competitive concept and quality oriented, improving technology, globalization of the university and formation of management knowledge will draw a new space in higher education institutions, which requires new roles and competencies of faculty members. In such a situation, the role of teachers has become more complex and unpredictable and faculty members need new and appropriate competence with today’s environment so that they could be able to overcome the challenges ahead. Therefore, we believe that the specifications and position ad must be based on up to date competence and ability.
In our opinion, competency-based advertisement will provide a targeted recruitment and will create a set of clear expectations for the potential applicants. The text of the ad is also very important because it effects on the type and the quality of applicants who respond to the advertisement. There must be enough information in the ad so the people can sift themselves if they are not suitable for the job. It also prevents managers from wasting time.
In the case of position advertising, we believe that advertising should be broad and proactive in order to attract applicants for faculty members because researches show that Proactive advertising increases the chances of recruiting suitable applicants. Therefore, in order to recruit diverse applicants, we should consider different and variety places and scenes consider for the position advertised.
About the recruitment criteria, we believe that for the position which, we are looking for someone to occupy it, the competencies and required qualities for the position and the relative weight of each of them should be discussed and consensus. Consensus about the faculty members applicants’ evaluation criteria are different that it depends on the nature of the position, university or field standards and the needs of the group. In doing so, we must be considered the needs and wishes of the committee members, educational department, university and students as well as position type (educational, research, clinical …). In addition to the traditional criteria such as degree, research field, publication records and teaching experience, evidences such as experience of successful mentoring and tutoring, participation in various populations and other criteria that are important for the university should be considered.
About the evaluation tests, the applicants’ reviewing must be complete and comprehensive as possible and according to the role and responsibilities of the faculty member in each educational department;an appropriate evaluation method should be considered. These assessments can be included,items for example the guidance on a morning report in role-playing, the translation of a scientific paper and working with computers in addition to the mentioned items.
This study shows that the interview is the most common faculty members’ applicants’evaluation way that is conducted in two forms of preliminary screening interview and the interview at the University. We believe that the initial screening interview is an effective way to lower the applicants’source and restricting it to applicants who have the highest correlation with the description of position and it is better to be considered in the process of selection and recruitment. We believe that an interview must also be structured, because it provides a fair evaluation and same questions will be asked of all applicants and bias will decrease in recruitment. The research results show that two methods of interview (competency-based and value-based) are considered for the faculty members. These two types of interviews are similar in terms of question structure. Competency-based interviewing is a new and unbiased interview that analysis the potential competencies of applicants by reviewing the used skills in the past performance (20). Competency-based interview questions wording is different from the traditional interviews. In traditional interviews, questions are generally asked, for example, talk about yourself. But competency -based questions often begin this way: explain about a situation when … or describe a situation that…. We believe this kind of wording encourages applicants to show how he expressed his strengths and weaknesses in real terms.
Such responses are much more useful than the skill description because it provides insight on how the applicant uses his skills. Different competencies such as personal characteristics (flexibility, determination, independence, risk-taking, personal integrity), managerial, analytical, interpersonal and motivational capabilities (28), professionalism, critical thinking, creativity, communication skills and teamwork (20, 29, 30) can be evaluated this way.
Through value-based interviews with the different values such as caring, commitment, cooperation, accountability, trusteeship and … can be evaluated (18). We believe that these two interviews could assess the applicants after the value and attitude as well applicants’ competencies.These types of interviews are more objective than other interview techniques in decisions, and a variety of competencies, which is necessary for faculty members as well as all types of values that are the key dimension to enter the university,can be evaluated through these two interviews.
Research from referrals, reviewing the legal profile of the individual, the workplace or education place is appropriate methods for assessing the values and applicant’s abilities. We believe that the faculty member who is responsible for training students should be ethical and law oriented. The use of referrals’ reason is also this belief that the past performance will predict the future performance. In addition to exploring the information from the applicant’s resume, the committee members can use the applicant’s checking in order to verify and assess the competencies and features that an applicant has provided. In our view, talking with students who interact with the applicant also provides very good information in this area. Referrals may also be asked if they know someone else who can give us information about this applicant. This method is a good way that we don’t search individuals that the applicant has mentioned as a referral.
We believe that in the final applicants’ evaluation, we should put various sources of information together from a proper perspective and make the final decision according to our need. We should pay attention to this issue that why some information is not consistent with the rest. Applicants’ suggestion should be performed after a detailed and complete attention to all evaluation information of each committee member, referrals’ feedback and informed talking among members at the meeting that all members of the committee are in it.
In the welcoming stage of the new hired person or the justification stage, it is also important that most universities do not pay enough attention to it. Familarization purposes, including socialization, gaining strength and exposing to organizational culture. Researches show that socialization leads to positive outcomes, such as higher job satisfaction, better job performance, more organizational commitment, and reduce the desire to leave the organization (31).
As for the faculty members’ recruitment models, we believe, in various mentioned models, the emphasis is on competencies and it can be said that most models are considered the competency from three dimensions of knowledge, skills and competencies and attitudes and values. In most research models, the attitudes and values dimension is considered. For example, in the University of Nottingham model the values dimension is named as core values, in the University of Manchester named as morality issues, in Nelson’s model named as personality traits and basic skills, in Badger’s model named as main values and in Johnson’s model named as a virtue. Nelson, Badger and Johnson believe that values dimension in competence dimensions is the most important and the most basic dimension.
The competency dimension is considered in all models. Some models have only referred to the core competencies such as the Johns Hopkins University model, but the University of Nottingham uses the a more comprehensive model and consider management competencies in addition to core competencies in the recruitment of faculty members.
The knowledge dimension is considered as one of the competency dimensions in the models of Nottingham, Manchester, Nelson and Johnson. In our opinion, all recruitment models’ emphasis on capabilities and competencies, recall the competency-based management model of the mind. In the context of human resource management, the competency-based management is mentioned. Competency-based management is the application of a set of competencies for human resource management as this performance participates in an effective and efficient way to fulfill the mission, goals and strategies of the organization. This model will build a basis for core processes and activities of human resources management and regarding the creation a source of talented and capable people that can meet the organization strategic goals effectively will help to improve the application. Also, this model provides clear and common required expectations for each value and capability and will focus on the recruitment of the evaluation methods (32). Competencies are components of competency-based management. Various definitions come out of competence:
– Knowledge, skill, ability or related characteristics with high performance in a job
– A combination of knowledge, attitude and required skills to perform such a role effectively
– Any knowledge, skills, abilities or personal qualities that are shown through behavior and lead to the excellence of service
Various categories are also considered for competencies that the most common is in the field of human resources management Bonder’s category. He put the competencies into three categories:
The core competencies: a set of key and common competencies for all job levels in the organization. These competencies are arisen from the mandate, mission and organizational values .
Functional Competencies: a set of competencies that is essential for all employees that do a common task and are in a common class or job group.
Task competencies: a set of characteristics and professional requirements that is considered in a specific job (24).
We believe that from the different definitions that are given for competency, it can be concluded that, firstly: the competence has a general concept that can involve attitudes, values, knowledge, skills and abilities. Secondly, competencies are more detected based on the individual’s visible behavior.
We believe that the competencies of the faculty members can be categorized in the three groups of attitudes and values, skills and abilities, knowledge and awareness. We believe that in the recruitment of faculty members, core values that stem from the mission, values and culture of every university should be considered so that it will have a synergistic role to fulfill the organizational missions. Moreover, core competencies and dependent competencies on the duty should be considered for the recruitment of faculty members. In our view, having the core competencies is required for all faculty members, such as the ability of analysis and decision-making, communication, teamwork. Dependent competencies on the duty are also that the competencies that are determined according to the role and expected task of the faculty member, such as educational competencies, research competencies. We also believe that values, competencies and sub competencies must be defined and indicator behaviors of each value and competency also represent so that it could be a basis for evaluation and be measurable.
We like Badger, Nelson and Johnson believe that values and attitudes are the most important aspect in choosing faculty members, and we believe that the value system of people is the most difficult part to change and in our view, the attitudes and values dimension is as the basis dimension that is a background to enter the university. Competency-based management model will provide a complete picture of the job requirements for inclusion in the position ad and can ensure the interview process and systematic and focused recruitment. This model provides a more targeted selection and recruitment and creates a set of clear expectations for the potential applicants. With this model, the selection and recruitment committee will be able to evaluate better the applicant’s competencies and values and to maximize the chances of finding qualified applicants. Also, they support the information about competencies through a variety of evaluation ways of each other and increase the quantity and quality of obtaining information from the applicant. We believe that by using a 13-steps systematic process of selection and recruitment, having a proactive recruitment committee, capable and versatile, setting the position description based on competency, using a variety of applicant tracking, advertisement based on competency and ability, evaluation of applicants with new Competency-based and value-based interviews methods and adopting competency-based recruitment model, accessing and selecting qualified and capable forces can be possible in the university (Figure 1).
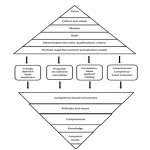 |
Figure 1 |
Competing Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the vice-chancellor on research in Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences who approved and financially supported this study.
Refrences
- Abtahi H, Aarabi M, Jafarinia S, Najjari R. Human resource management strategies. first ed.Tehran: pouy; 2008.
- Armstrong M. Strategic human resource management a guide to action. 3 rd ed. London2006.
- Malik S, Waheed A, Tufail S, ZameerH, Mehboob H. Issues and Problems Faced by Organizations in Recruitment. IJBMT 2012 2(5):1-7.
- Moradi M, Zanjani B. Designing a threefold skills model for selecting Mmanagers through multi-criterion decision-making approach. Human resource management researches. 2014 5(2):1-30.
- Mirsepasi N. Human resource strategic management&labour relations 3 rd ed. Tehran: Mir; 2013.
- Stutz F P, Warf B. The World Economy: Resources, Location,Trade, and Development. Fifth ed: Prentice Hall; 2007.
- Bamberger P, Meshoulam I. Human resource management strategy. Tehran: Cultural Research Office; 2000.
- Hashemi MM. Analysis the management of universities and institutions of higher education in recent years 2012. Available from: http://www.imna.ir/vdcayon0.49nuo15kk4.html.
- Mehralizade Y,Sepasi H , Omidian F. Investigation the relationship between organizational commitment and participation of faculty members in academic decisions. Quarterly Journal of Research and Planning in Higher Education 2006;11(2):1-36.
- Grant M, Bootht A. Atypology of reviews:ananalysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information and Libraries Journal. 2009;26:91-108.
- University of California. Recruitment and Appointment Guidelines 2013. Available from: http://www. berkeley.edu/resources/faculty_search_guide.pdf.
- University of Karolinska. 2015. Available from: https://internwebben.ki.se/en/recruit-and-employ-0.
- University of Western Australia. Selection and appointment guide for the chair of selection committees 2012. Available from: : http://www.hr.uwa.pdf.
- University of Washington. University of Washington Faculty Search Committee Briefing Handbook 2012. Available from: https://www.tacoma.uw.edu/…/UW_Search_Committee.
- University of Loyola Marymount. Best practices: recruiting and hiring faculty for mission 2009. Available from: http://www.lmu.edu/Assets/Academic Affairs/ I.pdf.
- Vicker LA, Royer HJ. The Complete Academic SEARCH MANUAL A Systematic Approach to Successful and Inclusive Hiring. First Ed. ed. USA: Stylus; 2006.
- Fine E, Handelsman J. Searching for exellence and diversity. second ed. ed. University of Wiscansin: WISELI; 2012.
- Lee VS, Pershing DW. Faculty Search and Recruitment Toolkit University of Utah2012.
- university of Nattingham. Competency Based Recruitment and Selection(A Handbook for Managers) 2010. Available from: http://www.ntu.ac.uk/cpld/document_uploads/98694.pdf.
- Switt JT. Hiring the right person the first time: tips on conducting a job interview. Journal of The American Dietetic Association. 2008;108(7):1118-20.
- selection Tssbo. Selection criteria and how to attract employees in some countries Iran,Tehran2014. Available from: http://gozinesh.org.ir/Portal/home/generaltext.2014.
- Middlewood D, Lumby J. Human Resource Management in Schools and Colleges. London: Cromwell Press; 1998.
- University of Johns Hopkins. Talent Management USA: JHU Human Resources; 2010. Available from: http://tmod.jhu.edu/talent_mgmt/talent_mgmt.cfm.
- Chitsaz E. Faculty competence model of Higher Education Institutions Tehran Office Publisher cultural studies and social planning Ministry of Science, Research and Technology; 2011.
- Hand JS. Identification of Competencies for Effective Dental Faculty. Journal of Dental Education 2006;70(9):937-74.
- Badger W, Smith J. Profiling faculty candidates: The reality of unofficial rankings in recruiting. . ASC Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference; 2006; Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado.
- Johnson B. A Framework for Conceptualizing Competence to Mentor. Ethics & Behavior. 2003;13 (2):127-51.
- Simpson B. Guide to competency based interviews 2014. Available from: www.barclaysimpson.com.
- University of Delware, Career services center. 2014.
- University of Washington. behavioral interview 2014. Available from: http://www.washington.edu/admin/hr/roles/mgr/hire/interview-select/behavioral.html.
- Pololi LH, Krupat E, Civian JT, Ash AS, Brennan RT. Why Are a Quarter of Faculty Considering Leaving Academic Medicine? A Study of Their Perceptions of Institutional Culture and Intentions to Leave at 26 Representative U.S. Medical Schools. Academic Medicine. 2012;87(7):859–69.
- Ennis M. Competency Models: A Review of the Literature and The Role of the Employment and Training Administration (ETA). U. S. Department of Labor: 2008.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





