How to Cite | Publication History | PlumX Article Matrix
Biological Effect on Adhatoda Vasica Extract and its Combination with Antibiotics
Jigar S. Patel*1![]() , Vikas R. Shukla2, Bhavya S. Salvi1, Piyush J. Vyas 2
, Vikas R. Shukla2, Bhavya S. Salvi1, Piyush J. Vyas 2 ![]() and Chintu J. Patel1
and Chintu J. Patel1
1Dr.Indu Dayal Meshri College of Science and Technology, Patan
2Sheth M. N Science College, Patan, Gujarat, India
Corresponding Author E-mail : jjjigar007@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bbra/2829
ABSTRACT: Extract of many plants proved potent antimicrobial interest against bacteria and Fungi. Adhatoda Vasica use as a therapeutic plant for various diseases since prehistoric eras. Mixture of plant extracts and antibiotics were used to increase sensitivity of plant extract and lower side effect of allopathy tablets. Gradually, bacteria salvage antibody towards traditional antibiotics and becoming greater powerful. To prevent their stimulating power, combination of plant extracts and antibiotics suggest one of the high-quality consequences in such direction. If dependable plant extracts had been taken in proper doses, it is able to prove pleasant ancillary therapies for patient. This is in vitro look at and such mixture must be trailed with the aid of toxicity check and in vivo assessments to determine its therapeutic usage against the test organisms.
KEYWORDS: Adhatoda Vasica, Antimicrobial Study, Antibiotics
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Patel J. S, Shukla V. R, Salvi B. S, Vyas P. J, Patel C. J. Biological Effect on Adhatoda Vasica Extract and its Combination with Antibiotics. Biosci Biotech Res Asia 2020;17(2). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Patel J. S, Shukla V. R, Salvi B. S, Vyas P. J, Patel C. J. Biological Effect on Adhatoda Vasica Extract and its Combination with Antibiotics. Biosci Biotech Res Asia 2020;17(2). Available from: https://bit.ly/2A6V08W |
Introduction
Nature gives several things against several diseases since last many decades. (Samuelsson et al., 2017) Adhatoda Vasica is a perpetual plant having a place with family Acanthaceae, generally known as Vasaka. (Claeson UP, et al., 2000) It is a small evergreen, perpetual bush dispersed all through India. It has been utilized for the treatment of different infections and clutters, especially for the respiratory tract illnesses. It is recognized with an upsetting smell and bitter taste. (Maurya S, et al., 2010) Vasicine and vasicinone alkaloids are the significant chemical constituents of the plant and are liable for its solid respiratory energizer activity. (Rastogi RP, et al., 1999) The drug for the most part contains fresh or dried leaves however the flowers, foods grown from the ground are likewise broadly utilized for different illnesses. Different measurement types of leaf-like powder, fresh juice, decoction, alcoholic and aqueous extract, and so on., are portrayed to be utilized for different diseases. (Anonymous ,1985)
A.Vasica was especially utilized as a home-grown medication for treating respiratory grievance including cold, hack, incessant bronchitis, asthma and as antispasmodic. (Singh B, et al., 2013) It has been accounted for antibacterial, injury mending, hypoglycemic, abortifacient, antitussive, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities. (Ahmad S, et al., 2009) Most part contains phytochemical likes pyrroquinazoline alkaloids, flavonoids, triterpenes, (Atta-Ur-Rahman, et al., 1997) steroids, tannins, saponins and glycosides. (Yusuf M, 2016) Therefore, influencing the bacterial pathogenic potential through majority detecting restraint is one of the new methodologies that are utilized to battle the microbial resistance. (Bhardwaj K, et al., 2013) In laboratory experiments on cats and dogs, A. Vasica increases bile activity when animals are given a dose of 5mg / kg. in dogs, the amount of excreted bile increases by 40-100%. Animals also showed increased bilirubin excretion. (Gangwar et al. 2014)
In recent time medicine in surgery, cancer chemotherapy, and limb transplantation is credited to the use of antibiotics. (Livermore et al., 2002) Antibiotics working today will not work tomorrow New drugs must be examined, with fewer resistance (Sarkar et al., 2003) As a resistance to the spread of old antibiotics, new immune agents are rapidly developed. Yet, records of the rapid emergence and emergence of new antimicrobial agents suggest that a new family of antimicrobial agents will have a shorter life span. (Coates et al., 2002) For that much chemical contained the Adhatoda Vasica is effective against serval disease. Combination of plant extracts and antibiotics were used to increase sensitivity of plant extract and lower side effect of allopathy tablets.
Common Name
English : Malabar nut, Adulsa
Hindi : Adosa, Adalsa, Vasaka
Gujarati : Ardusi, Adusi
Marathi : Vasuka
Plant Anatomy (Flora of Gujarat state, 1978)
Kingdom : Plantae
Division : Angiosperm
Class : Dicotyledonae
Series : Bicarpellatae
Order : Personales
Family : Acanthaceae
Genus : Adhatoda
Species : Vasica
 |
Figures 1: Adhatoda Vasica Plant |
Materials and Methods
Material Use for Study
Adhatoda Vasica Plant
Antibacterial Antibiotics : Amoxicilline, Ciprofloxacin, Ceftazidime, Erythromycin
Antifungal Antibiotics : Amphotericin-B, Fluconazole
Bacteria : Bacillus subtilis (MTCC 441), Escherichia coli (MTCC 1687), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 1688), Staphylococcus aureus (MTCC 737)
Fungi : Aspergillus Niger (MTCC 1344), Candida albicans (MTCC 81)
Method
Leaves of the Adhatoda Vasica was conglomerate from local area of north Gujarat in June 2018. Identification of the plant was done by Dr. N. K. Patel, head of the botany department, Sheath M. N. Science college, Patan. The first stages of the study of medicinal plants are to prepare plant samples, which is to store biomolecules in plants before extracted. The leaves were thoroughly wash with tap water and then washed with deionized water to remove particles of dust and sand. The leaves were dried in the dark at room temperature for several days and then powder with mortar. And it is extracted by using Soxhlet extraction.
Qualitative Phytochemical Analysis
Following methods were used for analysis of different type phytochemicals.
Test for Alkaloids
Plant Extractions were dissolved in dil. HCl and filtered
Dragendroff’s Test
Plant extract + Potassium Bismuth Iodide solution (Dragendroff’s Reagent) → Orange Precipitate
Hagers’s Test
Plant extract + Picric Acid (Hagers’s Reagent) → Yellow Precipitate
Mayers’s Test
Plant extract + Potassium Mercuric Iodide solution (Mayers’s Reagent) → Cream precipitate
Wagner’s Test
Reaction of plant extract + Iodine in Potassium Iodide (Wagner’s Reagent) → Red-brown precipitate
Test for Flavonoids
Test with Alkaline
Plant extract + Sodium Hydroxide → intense yellow color
which become colorless on further adding Dil. acid
Test with Lead Acetate
Treat plant extract + few drops of Lead Acetate → Yellow color precipitate
Shinoda Test
Dried powder of plant + 5 ml of 95% CH3OH + Few drops of conc. HCl along + 0.5 g magnesium → turnings Pink precipitate
Test for Glycosides
Keller-Kiiani Test
Plant extract + gla. CH3COOH + few drops 5% FeCl3 + concentrated sulfuric acid → formation of blue color in acetic layer.
Legal Test
Dissolve plant extract in pyridine + sodium nitroprusside solution + made alkaline → Pink or red Color produce
Test for Phenolics
FeCl3 Test
Plant extract + aqueous FeCl3 → blue color
Test for Saponins
Foam Test
Plant extract in test tube with a little quantity of water → foam produced persisted for 10 minutes.
Test for Tannins
Gelatin Test
Plant extract + 1% Gelatin Solution containing 10% sodium chloride → White precipitate
FeCl3 Test
Plant extract + FeCl3 → Blue-black precipitate
Test for Terpenoids
Salkowski Test
Extract + Con. H2SO4 → formation of yellow colored at lower layer
Preparation of Combination
Activities of various extract and their combination were resolute by the zone of the inhibition method. It was investigated by agar diffusion method using agar cup method. Purified extract was diluted in dimethyl sulfoxide and purified antibiotics were used by purification; and stand at 40 C. For compare slandered results we used standard antibiotic. Antimicrobial activity of all extracts and their combination were tested against for some bacteria and fungi which was prepared in Acetone (CH3COCH3), Methanol (CH3OH) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH) solvents. Muller-Hinton agar plates were seeded with indicator bacterial and fungal strains, and incubated for 24 hours at 370 C. The sensitivity of microbial species to plant extracts was determined by measuring the resistance zone size on the agar surface.
Result and Discussion
Table 1: Qualitative Phytochemical Analysis
| Phytochemical | Name of Test | Acetone extract | Ethanol Extract | Methanol Extract |
| Alkaloids | Dragendroff’s Test | – | + | + |
| Hagers’s Test | – | + | + | |
| Mayers’s Test | – | + | + | |
| Wagner’s Test | – | + | + | |
| Flavonoids | Test with Alkaline | – | + | + |
| Test with Lead Acetate | – | + | + | |
| Shinoda test | – | + | + | |
| Glycosides | Keller-Kiiani Test | – | – | + |
| Legal Test | – | + | + | |
| Phenolics | FeCl3 Test | + | + | + |
| Saponins | Foam Test | – | + | + |
| Tannins | Gelatin Test | – | – | – |
| FeCl3 Test | + | + | + | |
| Terpenoids | Salkowski Test | + | + | + |
(+) shows the Positive result and (-) show Negative Result of the Test
Antimicrobial Analysis Adhatoda Vasica, Antibiotics and Combination both for 25 μl.
*Growth of the Bacteria and Fungi shown in table number 2 to table number 9 are in Millimeter (mm)
Table 2: Antibacterial activity of Adhatoda Vasica
|
Bacteria
|
Ac extract | EtOH extract | MeOH extract | |||||||||
| Concentration (µg/ml) | ||||||||||||
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | |
| S. A | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 |
| B. S | 7 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
| P. A | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 |
| E. C | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 |
In the above table three different solvent were used for biological study. The study for each solvent were done with four different concentration. Table shows methanolic extract of in 1000 µg/ml concentration gives highest growth Which is used to decide dosage for human body.
Table 3: Antibacterial activity of Adhatoda Vasica with Amoxicilline
| Bacteria
|
Amo | Ac extract + Amo | EtOH extract + Amo | MeOH extract + Amo | |||||||||
| Concentration (µg/ml) | |||||||||||||
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | ||
| S. A | 28 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 28 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 |
| B. S | 30 | 28 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 31 | 31 | 26 | 25 |
| P. A | 1 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 13 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 10 |
| E. C | 1 | 14 | 13 | 11 | 10 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 10 | 16 | 14 | 13 | 12 |
Amoxicilline which is an antibacterial antibiotic is combined with the plant. The study shows the combination with 1000 µg/ml in MeOH extract gives highest zone of inhibition.
Table 4: Antibacterial activity of Adhatoda Vasica with Ciprofloxacin
| Bacteria
|
Cip | Ac extract + Cip | EtOH extract + Cip | MeOH extract+ Cip | |||||||||
| Concentration (µg/ml) | |||||||||||||
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | ||
| S. A | 24 | 26 | 25 | 25 | 24 | 30 | 29 | 27 | 22 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 |
| B. S | 27 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 30 | 29 | 27 | 27 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 |
| P. A | 27 | 33 | 31 | 30 | 28 | 35 | 32 | 30 | 29 | 36 | 35 | 32 | 30 |
| E. C | 27 | 32 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 34 | 32 | 32 | 28 | 35 | 33 | 31 | 30 |
The mixture of Plant extract and ciprofloxacin in 1000 µg/ml gives good values in zone of inhibition of bacteria.
Table 5: Antibacterial activity of Adhatoda Vasica with Ceftazidime
| Bacteria | Cef | Ac extract + Cef | EtOH extract + Cef | MeOH extract + Cef | |||||||||
| Concentration (µg/ml) | |||||||||||||
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | ||
| S. A | 1 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 7 |
| B. S | 1 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| P. A | 5 | 13 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 10 | 19 | 17 | 14 | 13 |
| E. C | 16 | 22 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 26 | 25 | 23 | 21 | 27 | 24 | 22 | 19 |
Ceftazidime which is also an antibacterial antibiotic also gives effective results in methanol when it mixed with plant
Table 6: Antibacterial activity of Adhatoda Vasica with Erythromycin
| Bacteria | Ery | Ac extract +Ery | EtOH extract + +Ery | MeOH extract +Ery | |||||||||
| Concentration (µg/ml) | |||||||||||||
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | ||
| S. A | 16 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 19 | 22 | 21 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 21 | 20 | 19 |
| B. S | 22 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 21 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 21 |
| P. A | 1 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 14 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 15 | 13 | 11 | 10 |
| E. C | 5 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 19 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 15 |
Combination of plant extract and an antibacterial antibiotics Erythromycin gives good activity in higher concentration.
Table 7: Antifungal activity Adhatoda Vasica
| Fungi | Ac extract | EtOH extract | MeOH extract | |||||||||
| Concentration (µg/ml) | ||||||||||||
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | |
| A. N | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 |
| C. A | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 5 |
In this table antifungal activity of Adhatoda Vasica extract was studied in Acetone, Methanol and Ethanol solvent. Biological study in two fungi, Aspergillus Niger and Candida Albicans fungi shows increasing of zone inhibition in higher concentration. Methanolic extract shows higher activity then other two solvent.
Table 8: Antifungal activity of Adhatoda Vasica with Amphotericin B
| Fungi | Amp | Ac extract +Amp | EtOH extract +Amp | MeOH extract +Amp | |||||||||
| Concentration (µg/ml) | |||||||||||||
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | ||
| A. N | 14 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 14 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 |
| C. A | 8 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 18 | 16 | 13 | 12 | 19 | 17 | 14 | 13 |
An antifungal antibiotic Amphotericin B when combined with Adhatoda Vasica extract gives very good activity in 1000 µg/ml concentration.
Table 9: Antifungal activity of Adhatoda Vasica with Fluconazole
| Fungi | Flu | Ac extract + Flu | EtOH extract + Flu | MeOH extract + Flu | |||||||||
| Concentration (µg/ml) | |||||||||||||
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | ||
| 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | 25 µl | |
| A. N | 1 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 8 |
| C. A | 1 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 5 |
Fluconazole which is also an antifungal antibiotic also gives effective activity in higher concentration of the solvent.
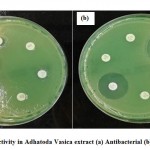 |
Figure 2: Activity in Adhatoda Vasica extract (a) Antibacterial (b) antifungal |
Conclusion
Plant drugs from Ayurvedic framework are being investigated globally. The consequences of the essential examination demonstrated that alongside its traditional helpful cases and some experimentally demonstrated pharmacological exercises, Adhatoda Vasica additionally has the possibility to be created as a powerful plant with combination of antibiotics. Combination of A. Vasica and antibiotics indicated pronounced antimicrobial activities with wonderful restraints. This work gives logical confirmations to medicinal uses of A. Vasica with commitment of a portion of the distinguished and tried phytoconstituents in the got organic impacts. From the study we find that the combination of plant extract with antibiotics gives very effective activity then only plant and antibiotics. It also suggests that methanolic extract with higher concentration gives best results than others.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to the Faculty member of Chemistry Department of Sheth M. N Science College, Patan. We are also thankful to the Microbiology Department of Dr. Indu Dayal Meshri College of Science and Technology, Patan for their kind support during the biological Study. We are also thankful to Dr. N. K. Patel, Head of Botany Department, Sheth M. N. Science College, Patan for identification of plant
Conflict of Interest Statement
We, the authors of the submitted manuscript declare that the work and data present in the manuscript entitled – qualitative analysis and biological study is genuine research carried out by us. The work finally belongs to the institutes. We have not misused the data previously published and have not manipulated the original work.
References
- Ahmad S, Garg M, Ali M, Singh M, Athar MT, Ansari SH. A phyto-pharmacological overview on Adhatoda zeylanica Medic. syn. A. vasica (Linn.) Nees, 2009.
- The Wealth of India, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, India. 1985; 76.
- Atta-Ur-Rahman, Sultana N, Akhter F, Nighat F, Choudhary MI. Phytochemical studies on Adhatoda vasica Nees. Natural Product Letters. 1997 Oct 1;10(4):249-56.
- K Bhardwaj A, Vinothkumar K, Rajpara N. Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors: attractive alternatives for control of infectious pathogens showing multiple drug resistance. Recent patents on anti-infective drug discovery. 2013 Apr 1;8(1):68-83.
- Claeson UP, Malmfors T, Wikman G, Bruhn JG. Adhatoda vasica: a critical review of ethnopharmacological and toxicological data. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2000 Sep 1;72(1-2):1-20.
- L Shah., Flora of Gujarat state. 1978, 1,48.
- Gangwar AK, Ghosh AK. Medicinal uses and pharmacological activity of Adhatoda vasica. International journal of herbal medicine. 2014;2(1):88-91.
- Livermore DM. Antibiotic resistance in staphylococci. International journal of antimicrobial agents. 2000 Nov 1;16:3-10.
- Maurya S, Singh D. Quantitative analysis of total phenolic content in Adhatoda vasica Nees extracts. International Journal of PharmTech Research. 2010 Oct;2(4):2403-6.
- Rastogi RP, Mehrotra BN. Compendium of Indian medicinal plants Vol. 2. Central Drug Research Institute; 1999,14.
- Samuelsson G, Bohlin L. Drugs of natural origin: a treatise of pharmacognosy. CRC Press Inc.; 2017.
- Sarkar A, Kumar KA, Dutta NK, Chakraborty P, Dastidar SG. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of dobutamine hydrochloride. Indian journal of medical microbiology. 2003 Jul 1;21(3):172.
- Singh B, Sharma RA. Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties of pyrroloquinazoline alkaloids from Adhatoda vasica Nees. Phytomedicine. 2013 Mar 15;20(5):441-5.
- Yusuf M. Adhatoda vasika N. leaves extract: Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial activity. International Journal of Engineering and Allied Sciences; 2016.
| Abbreviations | |
| Amo: Amoxicilline | Cip: Ciprofloxacin |
| Cef: Ceftazidime | Ery: Erythromycin |
| Amo: Amoxicilline | Flu: Fluconazole |
| A. N: Aspergillus Niger | C. A: Candida Albicans |
| Ac: Acetone (CH3COCH3) | EtOH: Methanol (CH3OH) |
| MeOH: Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) |
|

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





