How to Cite | Publication History | PlumX Article Matrix
Formulation and Evaluation of Quetiapine Fumarate Sustained Release Tablets
V. RavichandIran
Department of Pharmaceutics, Vels college of Pharmacy India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: sen03mpharm@gmail.com
ABSTRACT: Sustained release tablets of Quetiapine fumarate were prepared by wet granulation method using different polymers polymers HPMC K 4M , HPMC K 100M & EC in different ratios(F1 to F7)Dissolution was carried out in 0.1N Hcl & pH6.2 buffer. Dissolution tests are performed for successive batches and polymers were changed in each formulation. For seventh formulation maximum %Drug release was observed, in which ratio of two polymers HPMC K 4M & ETHYL CELLULOSE is 1:2. The % Drug release was very poor for polymers HPMC K 100M when compared to polymers HPMC K 4M & ETHYL CELLULOSE is 1:2.The dissolution profile of final batch(HPMC K 4M & ETHYL CELLULOSE 1:2.)compared with reference product which were found to be comparable with the reference product
KEYWORDS: Quetiapine fumarate; HPMC K 4M; ethyl cellulose; Sustained release tablets
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: RavichandIran. V. Formulation and Evaluation of Quetiapine Fumarate Sustained Release Tablets. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 2009;6(2) |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: RavichandIran. V. Formulation and Evaluation of Quetiapine Fumarate Sustained Release Tablets. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 2009;6(2). Available from: https://www.biotech-asia.org/?p=8768. |
Introduction
The main objective of present study is to develop quetiapine sustained release tablets for the treatment of schizophrenia. Quetiapine acts by blocking D2 receptors in the dopamine pathways of the brain. Dopamine released in these pathways has less effect. Excess release of dopamine in the mesolimbic pathway has been linked to psychotic experiences. By blocking the dopamine receptors in this pathway quetiapine fumarate controls psychotic experiences.For decreasing the dosage regimen of drug sustained release quetiapine fumarate tablets are necessary, for this purpose formulations containing drug in a sustained release tablet are prepared and evaluated using standard recommended tests.
Materials and Methods
Quetiapine fumarate was prepared by wet granulation method using Lactose monohydrate ,Micro crystalline cellulose ,Sodium citrate anhydrous ,HPMC K 100M ,HPMC K 4M,EC, Magnesium stearate. Preformulation studies of pure drug and mixed blend were carried out using organoleptic character, angle of repose ,bulk density, tapped density,carr’s index,and fourier transform spectroscopy. After compression the tablets were evaluated for thickness, hardness, friability, weight variation, drug content uniformity and invitro dissolution studies
Characterization of tablets
The properties of enteric coated tablet, such as thickness, hardness, friability, weight variation and content uniformity were determined using IP procedure.
Preparation of sustained release tablets
Drug, lactose, MCC cyclocel (101) passed through sieve no. ≠40. Sodium citrate anhydrous was passed through sieve no≠30 along with polymers. Magnesium stearate was passed alone through sieve no ≠40 and kept a side. All the ingredients along with drug and lactose, MCC (cyclocel), sodium citrate anhydrous, magnesium stearate mixed Except magnesium stearate all the ingredients are mixed in the 900 ml bowl with an impellor speed of 300 rpm and a chopper speed of 1000 rpm for 2 min. With the same mixing speed water was added with 7 ml/min until a granulate was formed. Drying was done overnight in an oven at 60º temperature. Granules of different sizes are passed through sieve no ≠20 mesh. Lubricant magnesium stearate is added to improve the free flowing property of granules. Compression was done in the punch size of 19.45×9.25mm s/c.
Results and Discussion
Preformulation studies are carried out and the results are tabulated
Evaluation of quetiapine fumarate granules
Physical evaluation
The bulk density, tapped density, compressibility index were observed as It reveals that all formulations blend having better flow characteristic and flow rate than raw material. Compare to all these formulations, formulation 7 having a good flow properties. So this formulation is selected for further process.
Evaluation of quetiapine fumarate tablets
Four formulations of uncoated tablets were evaluated for physical appearance, weight variation, thickness, hardness, and friability, disintegration time,drug content,and in vitro dissolution studies and the results are tabulated. Among the all seven formulations F7 was found to be correlated with the specified limits.
Table 1: Flow properties of Granules.
| Batch no | Angle of repose | Bulk Density
(gm/ml) |
Tapped Density
(gm/ml) |
% Compressibility |
| F1 | 39°.16” | 0.542 | 0.680 | 20.29 |
| F2 | 37°.25” | 0.621 | 0.7623 | 18.53 |
| F3 | 36°.18” | 0.603 | 0.735 | 17.95 |
| F4 | 35°.13” | 0.6412 | 0.7320 | 12.40 |
| F5 | 28°.11” | 0.684 | 0.757 | 9.64 |
Table 2: Physical parameters of tablets of each batch.
|
Formulation number |
Average Weight
(mg) |
Thickness
(mm) |
Hardness
(kp) |
Friability
(%) |
| F1 | 1062 | 6.7 | 15.2 | 0.21 |
| F2 | 1057 | 6.75 | 14.3 | 0.12 |
| F3 | 1083 | 6.75 | 14.8 | 0.48 |
| F4 | 1098 | 6.77 | 14.5 | 0.19 |
| F5 | 1069 | 6.99 | 16.3 | 0.24 |
| F6 | 1100 | 6.44 | 16.1 | 0.32 |
| F7 | 1083 | 6.18 | 14.9 | 0.29 |
Table 3: Dissolution profiles of marketed product (seroquel xr) in 0.1N HCl and 6.2 buffer.
| Time in hrs | Cumulative % Drug release |
| 2 | 31 |
| 6 | 48.8 |
| 8 | 57.9 |
| 12 | 68.9 |
| 16 | 75.1 |
| 18 | 81.8 |
| 20 | 87.4 |
| 22 | 92.6 |
| 24 | 99.3 |
Table 4: Dissolution profile (F 1) of quetiapine fumarate using HPMC k100m as a polymer.
| Time in hr | Cumulative %Drug release |
| 2 | 39.2 |
| 6 | 62.3 |
| 8 | 84.5 |
| 12 | 92.8 |
| 14 | 99.2 |
Table 5: Dissolution profile (F2) of quetiapine fumarate using hpmc k 4m as polymer.
| Time in hr | Cumulative %Drug release |
| 2 | 32.9 |
| 6 | 59.1 |
| 8 | 75.8 |
| 12 | 89.6 |
| 14 | 99 |
Table 6: Dissolution profile (F3) of quetiapine fumarate by using hpmc k100m & hpmc k 4m 1:1 ratio.
| Time in hr | Cumulative %Drug release |
| 2 | 33.4 |
| 6 | 55.5 |
| 8 | 71.4 |
| 12 | 87.1 |
| 16 | 99.1 |
Table 7: Dissolution profile (F4) of quetiapine fumarate by using hpmc k100m & ethyl cellulose in 1:1 ratio.
| Time in hr | cumulative %Drug release |
| 2 | 31.4 |
| 6 | 49.1 |
| 8 | 65.9 |
| 12 | 77.6 |
| 16 | 83.4 |
| 18 | 92.3 |
| 20 | 99.3 |
Table 8: Dissolution profile (F5) of quetiapine fumarate by using Hpmc k100m & ethyl cellulose in 1:2 ratio.
| Time in hr | Cumulative %Drug release |
| 2 | 32.7 |
| 6 | 49.9 |
| 8 | 55.3 |
| 12 | 68.6 |
| 16 | 79.8 |
| 18 | 85.3 |
| 20 | 91.8 |
| 22 | 99 |
Table 9: Dissolution profile (F6) of quetiapine fumarate by using hpmc k 4m & ethyl cellulose in 1:1 ratio.
| Time in hr | Cumulative %Drug release |
| 2 | 33.1 |
| 6 | 53.8 |
| 8 | 67.1 |
| 12 | 79.3 |
| 16 | 86.5 |
| 18 | 94.1 |
| 20 | 99.6 |
Table 10: Dissolution profile (F7) of quetiapine fumarate using hpmc k4m & ethyl cellulose in 1:2 ratio.
| Time in hr | Cumulative %Drug release |
| 2 | 31 |
| 6 | 48.8 |
| 8 | 57.9 |
| 12 | 68.9 |
| 16 | 75.1 |
| 18 | 81.8 |
| 20 | 87.4 |
| 24 | 99.5 |
Table 11: Comparisons of dissolution profile of f3, f4, f5, f6, and f7 prepared with the polymers hpmc k 100m, hpmc k 4m & ethyl cellulose in different ratios:
| Time (hrs) | HPMC 100M & 4M 1:1 ratio F3 | HPMC 100M & EC 1:1 ratio
F4 |
HPMC 100M & EC 1:2 ratio
F5 |
HPMC 4M & EC 1:1 ratio
F6
|
HPMC 4M & EC 1:2 ratio
F7
|
| 2 | 33.4 | 31.4 | 32.7 | 33.1 | 31 |
| 6 | 55.5 | 49.1 | 52.9 | 53.8 | 48.8 |
| 8 | 71.4 | 65.9 | 55.3 | 61.1 | 57.9 |
| 12 | 87.1 | 77.6 | 68.6 | 75.3 | 68.9 |
| 16 | 99.1 | 83.4 | 79.8 | 82.5 | 75.1 |
| 18 | 92.3 | 85.3 | 88.4 | 81.8 | |
| 20 | 99.3 | 91.8 | 93.6 | 87.4 | |
| 22 | 99 | 99.6 | 92.6 | ||
| 24 | 99.5 |
Table 12: Comparison of dissolution profile of f7 with marketed product seroquel xr-400.
| Time in hrs | Cumulative %Drug release formulation F7 | Cumulative % Drug released SEROQUEL XR-400 |
| 2 | 31 | 30.9 |
| 6 | 48.8 | 51.2 |
| 8 | 57.9 | 62.2 |
| 12 | 68.9 | 73.2 |
| 16 | 75.1 | 82.6 |
| 18 | 81.8 | 86.1 |
| 20 | 87.4 | 90.7 |
| 22 | 92.6 | 94.9 |
| 24 | 99.5 | 99.3 |
Table 13: Physical parameter evaluation (Stability study conducted at 40oc ±2oc/75% RH ±5%.)
| Test | Before | After 90 days | Inference |
| Hardness
Avg Weight Thickness Friability |
14.8KP
1049gm 6.26mm 0.29%
|
14.8KP
1049gm 6.26mm 0.28%
|
No significant change was observed |
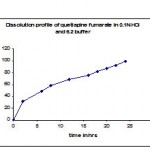 |
Figure 1
|
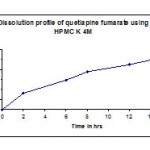 |
Figure 2
|
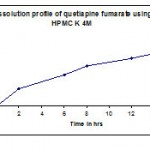 |
Figure 3
|
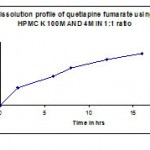 |
Figure 4
|
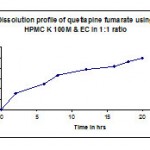 |
Figure 5
|
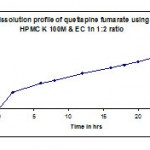 |
Figure 6
|
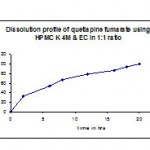 |
Figure 7
|
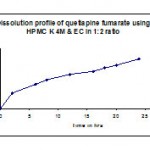 |
Figure 8
|
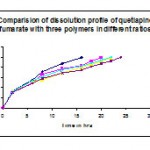 |
Figure 9
|
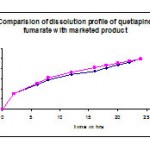 |
Figure 10
|
Conclusion
Dissolution test for innovatory tablets are performed in 0.1N Hcl & 6.2 buffer. Dissolution tests are performed for successive batches and polymers were changed in each formulation. For seventh formulation maximum %Drug release was observed, in which ratio of two polymers HPMC K 4M & ETHYL CELLULOSE is 1:2. The % Drug release is very poor for polymers HPMC K 100M. The formulation with best % Drug release was compared with marketed product values.
The stability of product was determined by conducting accelerated stability testing in 40°c ± 2°c / 75% ± 5%RH conditions for 3 months as per ICH guidelines in PVC/PVDC blisters. Finally after the duration, the product was analyzed for physical appearance, dissolution, assay. By the stability studies the formulated quetiapine fumarate sustained release tablets were proved to be stable throughout the period of storage. Formulated quetiapine fumarate sustained release tablets by using polymers HPMC K 4M & EC in 1:2 ratio were found to be stable through out its shelf life and comparable with reference product.
References
- Korinde Annemarie Jansen “pharmaceutical composition of quetiapine fumarate”.
- Pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment and/or prevention of schizophrenia and related disease.
- Method of manufacturing from “pharmaceutical composition of quetiapine fumarate” by korinde annerie.
- Journal of child and adolescent psycho pharmacology Dec 1, 2001
- Successful rechallenge with olanzapine International Journal of Psychiatry in Clinical Practice 9:4, 296-298.
- Quetiapine fumarate drug information and side effects are from www.wellsphere .com.
- sumegi A “quetiapine fumarate” neuropsychopharmacol hung 2008 Dec 10.
- Cutler AJ et al “extended release quetiapine fumarate monotherapy in major depressive disorder: a placebo and duloxetine controlled study. J Clin psychiatry 2009 apr; 7.
- Grover M et al “atypical antipsychotic quetiapine in the management of severe refractory functional gastrointestinal disorders.” Spinger link .com.
- Datto C et al “self reported sedation profile of immediate release quetiapine compared with extended release quetiapine fumarate during dose initiation: a randomized double blind crossover study in healthy adult subject.” 2009 Mar 31.ELSEVIER .com
- Casuno CM et al “Randomized double blind study of extended released quetiapine fumarate in schizophrenia” AM J psychiatry 2009 May 1.
- Figuora C et al “pharmacokinetic profiles of extended release quetiapine fumarate compared with quetiapine fumarate immediate release.”ELSEVIER com.
- Mamo DC et al “quetiapine fumarate extended release versus immediate release formulation a positron emission tomography study.” Jclin psychiatry.com.
- American journal of psychiatry 158:360.
- Sparshatt A et al “quetiapine dose response relationship in schizophrenia.”
- Wobrock T et al “achieving symptomatic remission in out patients with schizophrenia a naturalistic study with quetiapine.”Acta psychiatr scand.2009 Mar 10.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





