How to Cite | Publication History | PlumX Article Matrix
Molecular Characterization of Black Pepper (Piper Nigrum) Using RAPD and SSR Markers
Remmia Raghavan1, S. Elumalai1, K. Nirmal babu2, and Shailaja Hittalmani3
1P.G. Research Department of Plant Biology and Biotechnology, Presidency College Chennai - 600 065 India.
2Dept of Crop Improvement and Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Spices Research, Calicut, Kerala - 673 012 India.
3Marker Assisted Selection Laboratory, Department of Plant Breeding and Genetics, UAS,GKVK, Bangalore - 560 065 India.
ABSTRACT: A set of 20 Piper nigrum (Black Pepper) accessions were screened to identify the extent of genetic diversity present at the Molecular level using RAPD and SSR markers.. Dendogram constructed based on molecular polymorphism unveiled considerable amount of diversity among the varieties. Among this the SSR markers were found to be useful in discrimination and identification of the genotypes as it gave more genotypic specific bands.
KEYWORDS: Piper nigrum; SSR; RAPD; genetic diversity
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Raghavan R, Elumalai S, Babu K. N, Hittalmani S. Molecular Characterization of Black Pepper (Piper Nigrum) Using RAPD and SSR Markers. Biosci Biotech Res Asia 2010;7(2) |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Raghavan R, Elumalai S, Babu K. N, Hittalmani S. Molecular Characterization of Black Pepper (Piper Nigrum) Using RAPD and SSR Markers. Biosci Biotech Res Asia 2010;7(2). Available from:https://www.biotech-asia.org/?p=9791 |
Introduction
Black Pepper (Piper nigrum. L) is one of the oldest spice know to the world P.nigrum belongs to the family piperacea. The tropical ever green forests of Western Ghats are considered as the center of origin of Black Pepper (1). The major center of diversity of the genus piper is central & Northern South America, where 60% of the species are distributed. More than 1000 Spps are included in the genus of which 115 are of Indian origin. Black pepper, the most popular spice is cultivated in about 21 countries including India, Indonesia, Brazil, Malaysia, Srilanka, Vietnam, Thailand, China, Mexico, Guatemala. In India, Black pepper is grown predominantly in the states of Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu & to a certain extent in Maharashtra, AndraPradesh, Andaman and Nicobar Islands and North Eastern states viz, Assam, Meghalaya, Manipur and Arunachal Pradesh.
Morphological characters have been used extensively to study diversity of different form in the past. In recent years, attempts to study biodiversity at molecular level have gained importance. Among DNA based approaches for crop-improvement, the first step of molecular is the use of molecular markers as a tool to detect the extent and structure of Genetic variation(3,4) Providing insight into the diversity of crop- varieties and potential contributions represented by their wild relatives.
Microsatellite markers have become the DNA markers of choice for a wide range of application in genetic mapping and genome analysis genotype identification of Variety protection (5)) seed purity evaluation and germ plasm conservation, diversity studies (6, paternity determination and pedigree analysis (7)give and quantitative trait locus analysis (8) and Markers assisted breeding(9) In measuring genetic diversity assigning lines to heterotic groups and genetic fingerprinting , Microsatellite provides Power of discrimination equal to greater than that RFLP in an more cost effective manner and case of study the objective of this study were to assess the extent of genetic diversity and relationship among 20 Piper nigrum genotypes.
Materials and Methods
Plant Materials and Dna Extraction
Five Land Races & 13 advanced cultivars & 2 wild accessions of Piper nigrum collected from IISR Experimental farm, Peruvannamuzhi were used in the present study (TABLE-1) DNA was extracted according to the CTAB method with Minor modifications(2). Leaf tissue of 2g was ground to fine powder in liquid N2, followed by incubation in 15 ml of preheated extraction buffer (4% W/V CTAB, 1.4 M Nacl, 100 mm Tris-HCL PH 800, 20mm EDTA, 1.4m Nacl, 100mm Tris-HCL, PH 8-0, 20 mm EDTA, 2% PVP & 0.1 % V/V & Mercaptoethanol) for 2hr at 550C. The homogenate was extracted once with chloroform: Iso- amyl alcohol (24:1) and centrifuged at 15000 rpm at 250C. Nucleic acids were precipitated in 0.6 volume of isopropanol and collected by centrifugation (15,000rpm, 15 min, 250C). The precipitate was dissolved in TE- Buffer (100Mm Tris HCL PH : 8.0, 1 mm EDTA). DNA was treated with bovine pancreatic RNase and extracted with phenol: chloroform (1:1) and chloroform: iso-amyl alcohol (24:1) in succession. DNA was quantified in a Fluorometer and dissolved to appropriate dilution in TE Buffer
Ssr and Rapd Primers
15 Rapd Primers And 9 Ssr Primers Were Used In The Study Are Mentioned In The Table2(A,B) As Follows. The Primers Were Obtained From Sigma –Aldrich,Usa.Pcr Reactions Were Carried Out In A Eppendorf Thermocycler
Table 1: Piper Accessoins used in the Present Investigation.
| S.NO. | NAME | PLACE OF COLLECTION |
| 1. | PANNIYUR- 1 | KANNUR |
| 2. | PANNIYUR- 2 | KANNUR |
| 3. | PANNIYUR 3 | KANNUR |
| 4. | PANNIYOR 4 | KANNUR |
| 5. | PANNIYUR 5 | KANNUR |
| 6. | SREEKARA | CALICUT |
| 7. | SHUBAKARA | CALICUT |
| 8. | POURNAMI | CALICUT |
| 9. | PANCHAMI | CALICUT |
| 10. | MALABAR EXCEL | CALICUT |
| 11. | THEVAM | CALICUT |
| 12. | GIRIMUNDA | CALICUT |
| 13. | SHAKTHI | CALICUT |
| 14. | KARIMUNDA | IDUKKI |
| 15. | KALLUVALLY | WAYANAD |
| 16. | KUTHIRAVALY | CALICUT |
| 17. | BALAN KOTTA | CALICUT |
| 18. | PERUM KODI | IDUKKI |
| 19. | Piper nigrum
(WILD5422 |
PALAGHAT |
| 20. | Piper nigrum
(WILD)5569 |
KANNUR |
Table 2: Operon Primers Which Showed Polymorphism For Developing RAPD Profiles .
| Sl. No. | Oligo Name | GC % | Sequence (5’-3’) |
| 1 | OPA08 | 60% | GTGACGTAGG |
| 2 | OPA02 | 70% | TGCCGAGCTG |
| 3 | OPA05 | 60% | AGGGGTGTTG |
| 4 | OPB20 | 60% | GGACCCTTAC |
| 5 | OPB14 | 70% | TCCGCTCTGG |
| 6 | OPE12 | 70% | TTATCGCCCC |
| 7 | OPE05 | 60% | TCAGGGAGGT |
| 8 | OPE06 | 60% | AAGACCCCTC |
| 9 | OPE18 | 70% | GGACTGCAGA |
| 10 | OPE20 | 60% | AACGGTGACC |
| 11 | OPF09 | 60% | CCAAGCTTCC |
| 12 | OPF10 | 60% | GGAAGCTTGG |
| 13 | OPM04 | 70% | GGGGGTTGTC |
| 14 | OPU17 | 70% | ACCTGGGGAG |
| 15 | OPW11 | 60% | CTGATGCGTC |
Table 3: List of SSR Primers used in the Study.
| Locus | Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
| PN A5 | F 5’ CTTCCAGACCAATAATCAACTT 3’
R 5’ ATCCCAAAATACACAACAATTC 3’ |
| PN B5 | F 5’ GTTTTGAATGGGTCGGTGAT 3’
R 5’ ATTGTTCTGATTTCTTCGTTATTG 3’ |
| PN B9 | F 5’ AGTATTGGTTGTTTCTCTC 3’
R 5’ ATGTAAAATCGATAGTCCTCA 3’ |
| PN E3 | F 5’ TTTGTGTCCTCTCCCTCTCC 3’
R 5’ AAGACTAAATAGGCAAGGCAAA 3’ |
| PN F 1
|
F 5’ ACTTCAGTGCTATTTTTATCTTCC 3’
R 5’ CCAACGCCCACTCTCAT 3’ |
| PN G11 | F 5’ TTACTAGTGTCCACCCCCACT 3’
R5’ TCGATGGAAAGTCACCCTCT 3’ |
| PN H4 | F 5’ CTTTTCCCACAATTCAGTCTCG 3’
R 5’ ACCCATGCGTGTATCTTCTCAG 3’ |
| PN D10
|
F 5’ GTGTTACCTTTGGGGCATTCA 3’ R 5’ TGTGTCAGGGCATCAAACC 3’ |
| PN H 8a | F5’ TGTGTCTTTTATATTTTTGATG 3’
R5’ TATTAGTAGTTCTCCCTTTTGA3’
|
source
Menezes., et al
Pcr Amplification For Rapd The PCR was performed in a 20µL reaction mixture comprising 50 ng of template DNA, 2µL 10X assay Buffer, 25 Mm Mgcl2 (1µL), 100 mm each DNTP’s (dATP, dGTP, DCTP and dTTP), .85 U Taq DNA polymerase 10 pmolar primer, PCR reaction were carried out on a perkin Elmer 9600 DNA thermal cycler, After a predenaturation step of 4min at 940C, amplification reaction were cycled 40 times at 940C for 1 min, 360C for 1 min and 720C for 2 min followed by 5 min at 720C, was followed by completion of the primer extension on an Eppendorf thermal cycler.
Pcr Amplification for Ssr
The PCR was performed in a 20µL reaction mixture comprising 20 ng of template DNA, 2µL 10X assay Buffer, 25 Mm Mgcl2 (1µL), 100 mm each DNTP’s (dATP, dGTP, DCTP and dTTP), .85 U Taq DNA polymerase 10 pmolar primer, PCR reaction were carried out on a perkin Elmer 9600 DNA thermal cycle.Temperature DNA was initially denatured at 940C for 5 min ,followed by 35 cycles of 940 C for 1 min denaturation ,primer annealing temperature between 570C to 680C FOR 1 min and 2 min primer extension at 720C.Final 5 min incubation at 720C was followed for completionof primer extension on an Eppendorf thermal cycler.
Gel Scoring and Data Analysis
Amplified DNA samples were analyzed by electrophoresis on 1.4% and 3%agarose gels in 1XTBE Buffer. Clear and well resolved bands were scored for presence (1or absence (O).(Fig:1) Statistical analysis was carried out using STATISTICA Package. The program used was treeing with raw input data. The main parameter, which guided the joining process, is unweighed pair group method with Arithmetic mean (UPGMA) & Euclidean distance was computed. The relationship among 20 Black Pepper accessions was portrayed graphically in the form of a Dendogram.
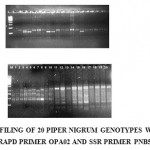 |
Figure 1
|
 |
Figure 2
|
Results and Discussion
Molecular profiles were developed with 15 RAPD Primers and 9 SSR primers Good polymorphism was observed between the genotypes for most of the primers studied. A total of 130 markers were obtained with 15 RAPD Primers .Out of which 71 markers were polymorphic and 51 were monomorphic. RAPD primer OPE-20 produced maximum numberof markers(13).Out of which 10 were polymorphic and 2 were monomorphic. Among the 9 SSR primers studied ,5 were Polymorphic(PNF1,PND10,PNA5,PNG11 and PNH8),rest of the primers produced Monomorphic(PNB5,PNE3,PNH4,PNB9,) bands.The PCR products were run on 4% Polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic system to check the extent of polymorphism. These polymorphic loci amplified approximately of size between 120-210bp.The maximum number of alleles amplified were at an average of 2 bands for each polymorphic primer pairs.
Conclusion
Grouping of individuals based on RAPD and SSR indicate a similarity in code region of the genome and hence common morphological traits. The molecular markers identified using RAPD and SSR techniques in the present study could be used in the identification of pepper genotypes quickly. Among this the SSR markers were found to the useful in discrimination and identification of the genotypes and it gave more genotypic specific bands. The genetic diversity obtained in this study might be useful in future strategies for evaluation of desired genotypes.Such molecular data would be useful for detecting DNA patterns unique for a given accession or a set of accessions . This will through some light on the pepper crop improvement and boost our domestic needs as well as the earnings of foreign exchange.
Acknowledgement
Deeply acknowledged to the Director IISR experimental form Peruvanamuzhi Calicut, Kerala for providing the plant materials for study.
This paper forms a part of PhD thesis ( Plant biology & Biotechnology submitted by Miss Remmia Raghavan to University of Madras, Nov 2010.
Referenc
- Hooker, J.D. 1886. The flora of British India Vol. 5. Todays and Tomorrows printers and publishers, New Delhi Pp .78-95.
- Williams J.G.K., Kubelik A.R. Livak, K.J. Rafalski J.A. and Tingey. S.V. 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are used as genetic markers. Nucleic Res., 18 6231 – 6235.
- Ibrahim K.K. Pillay V.S and Sasikumaran .S. 1984. Discriminant functions in distinguishing between Travancore & Malabar Cultivars of black pepper (pepper nigrums.L). Ind.Spices 21 and 22; 3-9.
- Ravindran P.N. and Nirmal Babu K. 1994. Genetic Resource of Black Pepper In; Chadha K.L, and Rethinum P (eds), Advances in Horticulture Vo1 9 Malhotra Publishing House, New Delhi, PP – 99-120.
- Li D., Rossnagel B.G. and Scoles G.J.2000.The development of oat microsatellite markers and their use in identifying Avena species and oat cultivars.Theor appl.Genet.,(in press)
- Senior M.L.,Murphy and J.P.,Goodman M.M .and Stuber C.W.1998.Utility of SSRs for determining similarities and relationships in maize using an agarose gel system.Crop.Sci.,38:1088-1098
- Xiao J.,Li J.,Yuan L.,McCouch S .R.and Tanksley S.D.1996.Genetic diversity and its relationship to hybrid performance and heterosis in rice as revealed by PCR based markers.Theor.Appl.Genetics.,92:637-643
- Van de Ven W.T.G. and McNicol R.j.1996 .Microsatellite as DNA markers in sikta spruce. Theor.Appl.Genetics .,93:257-261
- Koh H.j.,Heu M.H.and McCouch S.R 1996.Molecular mapping of the gene con trolling the super giant embryo character in rice. Theor.Appl.Genetics,93: 257-261
- Weising K.,Winter P.,Huttel B and Kahl G.1998.Microsatellite markers for molecular breeding .Journal of Crop production,1:113-143.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





